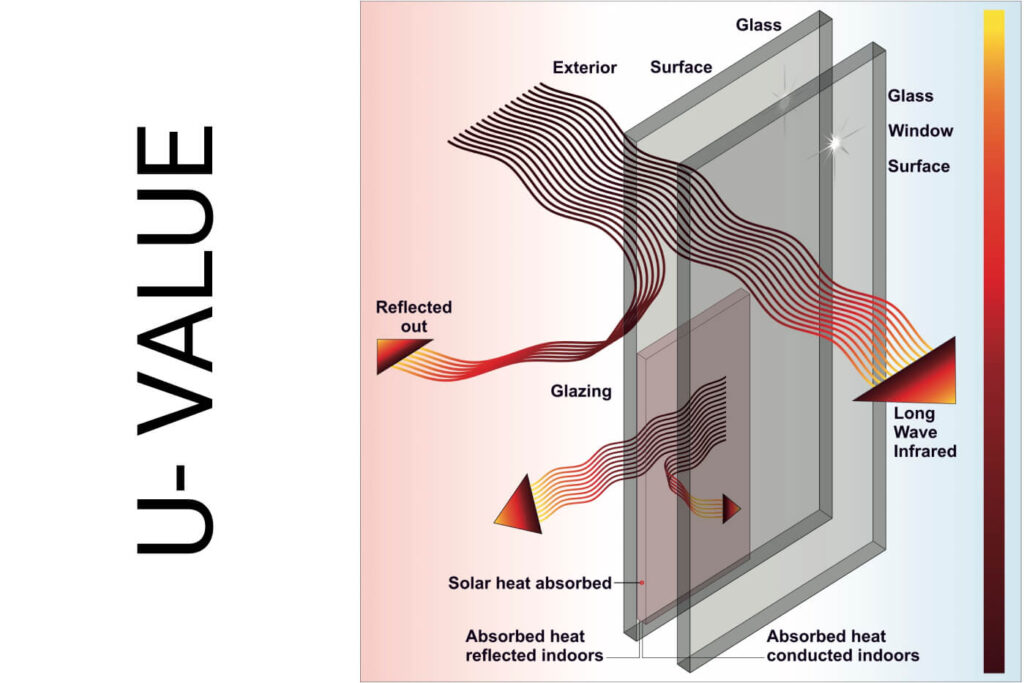
What is a good U-Value for windows?
When looking for windows, there is often a lot of technical information to consider, such as U-Values, which can be challenging to understand if you’re unfamiliar with the construction industry.
You may hear your installer or window manufacturer use the term thermal transmittance or U-Value, and this article will explain what it means, why it’s important, and what constitutes a good U-Value.
Along with appearance, one of the most critical aspects of a window for buyers is energy efficiency.
Windows that perform well thermally help maintain the internal temperature of your home by preventing excess heat transfer, reducing the need for additional power for heating, and ultimately lowering your energy costs.
Building elements like windows with better thermal performance not only improve comfort but also reduce annual heat loss, making your home more efficient.
Old windows, whether single or double-glazed, often suffer from poor thermal insulation, resulting in high U-Values and increased heat flow.

Understanding U-Value: A simple comparison
Think of a U-Value like a sieve. If the sieve has large holes, it lets more heat pass through easily—similar to a window with a high U-value, where heat escapes from your home quickly. In contrast, a sieve with smaller holes (a low U-Value) allows much less heat to pass through, which means it retains warmth better, keeping your home warmer during winter and cooler in summer.
Just like a well-insulated thermos bottle that keeps your drink warm by limiting heat loss, windows with a low U-Value limit heat transfer, making your home more energy-efficient. Therefore, you use less energy for heating and cooling, and as a result, your energy bills become lower over time.
For walls and roofs, a different measurement called the R-Value is often used, which measures thermal resistance—how well a material resists the flow of heat. A higher R-value means better insulation. While U-Values measure the rate of heat loss, R-Values indicate how well materials resist heat flow.
U-Value measure for different types of glazing
A U-Value measures how quickly heat passes through a window or other building material and is expressed in W/m²K.
Simply put, it shows how effective your windows are at keeping heat from escaping.
The lower the U-Value, the more efficient the window is at minimizing heat loss and keeping your home warm.
Windows with low U-Values offer better thermal resistance, meaning less heat is lost through the material, resulting in lower energy consumption.
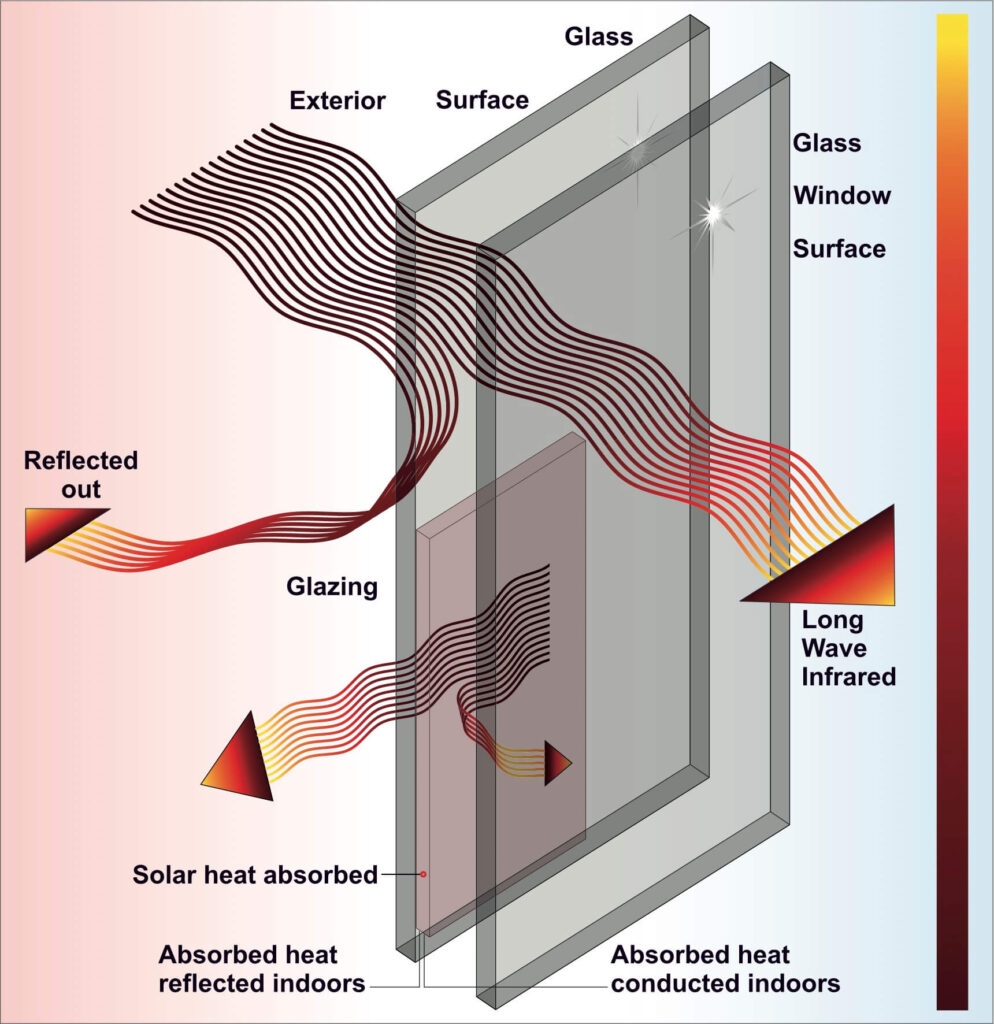
For example, old single-glazed windows can have U-Values as high as 5.8 W/m2K, while older double-glazed windows can have U-Values of around 2.8 W/m2K.
In contrast, modern windows are much more efficient, with replacement windows often boasting U-Values below 1.6 W/m2K, thanks to advancements in insulation material and window insulation technology.
Here’s a comparison of different types of glazing and their respective U-Values, along with their windows’ energy rating:
| Glazing Type | U-Value (W/m²K) | Thermal Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Single Glazing | 5.8 | Low |
| Old Double Glazing | 2.8 | Moderate |
| Modern Double Glazing | 1.6 or lower | High |
| Vacuum Double Glazing | 0.7 – 1.0 | Very High |
| Triple Glazing | 0.7 or lower | Very High |
U-Values for Single Glazing
Traditional single-glazed windows offer little thermal insulation, with U-Values of around 5.8 W/m2K, making them far less energy efficient than newer glazing options.
This high rate of heat transfer leads to more energy consumption and higher heating bills, as more power is needed to maintain a comfortable internal temperature.
U-Values for Double Glazing
Double glazing is now the standard for window replacements due to its balance between thermal performance and affordability. Double-glazed windows typically achieve U-Values below 1.6 W/m2K, with some even better depending on the frame and glass quality.
These windows reduce heat transmission significantly, helping keep your home warm and your energy bills low.
U-Values for Triple Glazing
Triple glazing, which uses three panes of glass, offers even greater thermal resistivity, achieving U-Values as low as 0.7 W/m2K.
This makes triple glazing highly effective for homes in colder locations or where enhanced thermal insulation is a priority. Although it provides superior thermal transmittance, it’s worth considering if it’s necessary for your region and building project.
U-Values for Vacuum Double Glazing
Vacuum double glazing is a highly efficient form of glazing that uses a thin vacuum layer between two panes of glass to minimize heat transfer. The vacuum acts as an excellent insulator, reducing thermal transmittance to a level similar to or better than triple glazing, but with a thinner profile.
With U-Values as low as 0.7 to 1.0 W/m²K, vacuum glazing offers superior thermal performance, making it ideal for properties that need to balance energy efficiency with retaining heritage features or slim window profiles.
What is the minimum U-Value for windows?
Since 2002, windows have had to comply with Building Regulations U-values. These regulations require replacement windows to have a U-value of 1.6 W/m2K or a C-rating.
This means they must reduce heat loss to a certain level. Windows with lower U-values are more effective at keeping heat inside your home, improving its overall energy performance.
When choosing windows, understanding U-Values and their role in heat transfer is essential for making an informed decision.
Whether you’re opting for single, double, or triple glazing, choosing windows with a low U-Value will significantly enhance the thermal efficiency of your home.
As a general guideline, aim for U-Values below 1.6 W/m2K to comply with regulations and ensure your windows contribute to a more energy-efficient home.
Read more articles

Sash window parts and anatomy
Sash window parts and anatomy
How long does double glazing last
How long does double glazing last
Common timbers for windows
Common timbers for windows